Market Research: NFC Payments
- nipunkapur5678
- Oct 26, 2024
- 3 min read
India has emerged as a global leader in the use of digital payments. India accounted for 46% of global real-time payments in 2022, more than the next four biggest countries combined. India leads the list of five countries in terms of digital payments, with 89.5 million transactions expected in 2022.(1) Almost 40% of payments (by value) are digital, contributing to a US$ 3 trillion digital payment market as a result of rapid digital infrastructure expansion, UPI-led migration to digital, pandemic-driven acceleration of shift in customer preferences, expanding merchant acceptance network, and disruptive innovations by fintech companies. India's digital payments industry has reached an all-time high and is expected to more than triple to US$ 10 trillion by 2026.(2)
Tier 3-6 cities are expected to drive the next wave of growth, since they have generated roughly 60-70% of new mobile payment clients in the last two years. Expanding merchant acceptance, digitising value chains, and developing a financial services ecosystem in underserved segments are the primary drivers of India's rapid adoption of digital payments. The adoption of embedded payments via 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT), as well as the implementation of India's sovereign digital rupee, are projected to provide additional impetus.
In India, digital transactions started around the 1980s with the launch of credit cards. The country saw a huge growth in awareness, the number of mobile phones and Internet users, and the number of digital payment mode users. With growing demand, newer businesses and applications came into existence. India has witnessed significant growth in the number of digital transactions since 2010. During FY 2010–11, the number of digital transactions in the country was 4.98 billion, valued at Rs. 96 lakh crores (approximately US$ 1.3 trillion). In FY 2020, the number of transactions surged to 16.23 billion, with the value increasing to Rs. 3,435 lakh crore (approximately US$ 45.9 trillion). This represented a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 43% in value and 12.54% in the volume of transactions over FY 2010–2020.
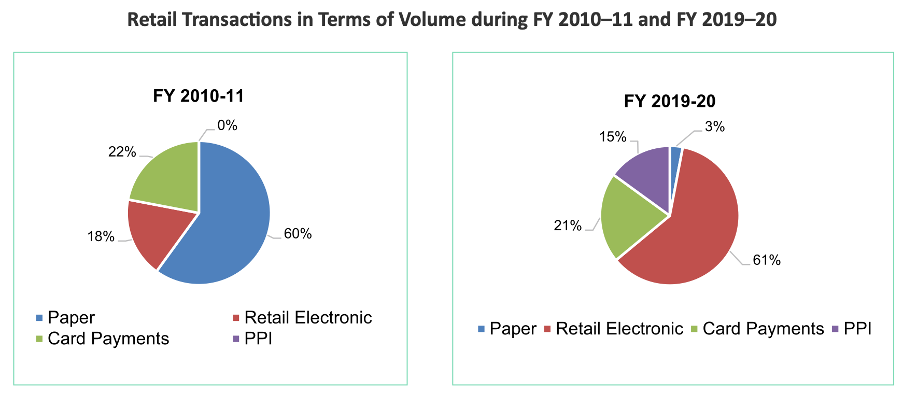
During FY 2010–11, the majority of transactions were conducted through the paper payment method, which accounted for 60%. The preferred method of transaction shifted towards the electronic mode during FY 2019–20; the digital payment mode accounted for 97% of the total payments and paper-based payments accounted for only 3%.

A similar trend can be seen in transactions in value terms.
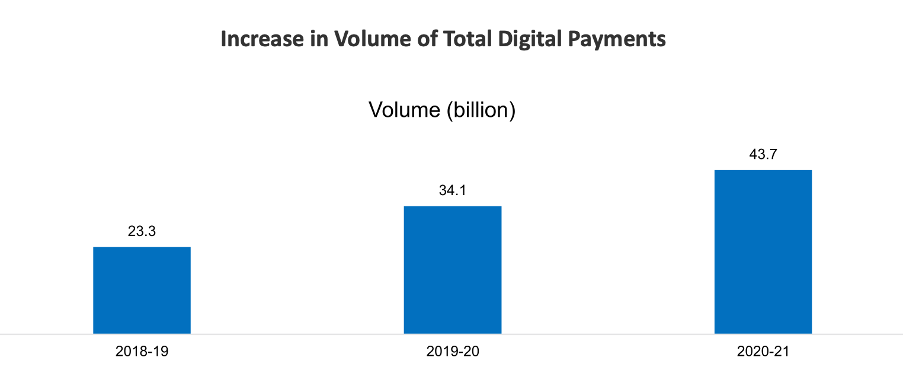
The volume of total digital payments increased from 23.3 billion during FY 2018–19 to 43.7 billion during FY 2020–21, representing an increase of 88% over the two years. The volume of non-cash payments increased to 98.5% during FY 2020–21 from 97% during FY 2019–20. This indicates the success and future potential of digitalization in India.
Launch of UPI and its impact:
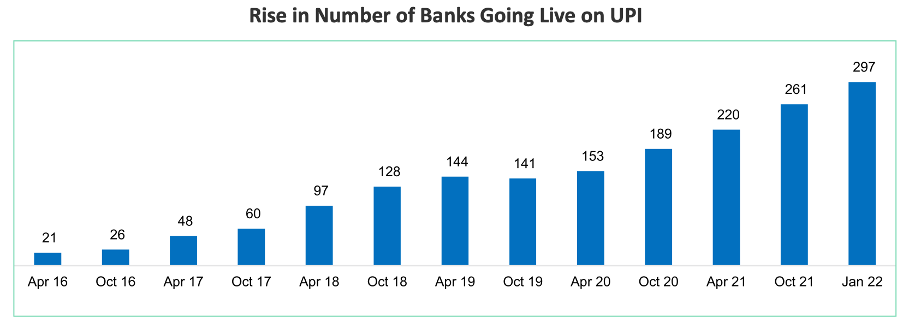
As of Jan 2022, a total of 297 banks are linked to the UPI platform; there are 46 payment service providers and 251 issuers.


The value of UPI transactions in India crossed US$ 100 billion in October 2021, reaching Rs. 7.71 lakh crore (approximately US$ 103 billion). In October 2021, the number of transactions was around 4.2 billion. This represented a CAGR of more than 700% from 2016.
Drivers Behind the Growth of NFC Technology:
Several factors have driven the adoption and growth of NFC technology in India:
Government Initiatives: The Digital India program, launched in 2015, has been instrumental in promoting digital payments. It aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society by ensuring the availability of digital infrastructure and services.
Mobile and Internet Penetration: The rapid increase in mobile and internet users has provided a substantial user base for digital payment systems. As of FY 2020, India had 16.23 billion digital transactions valued at approximately US$ 45.9 trillion.
Unified Payments Interface (UPI): Launched in 2016, UPI has significantly boosted digital transactions in India. The number of banks linked to UPI increased from 21 in 2016 to 297 by 2021, reflecting a CAGR of approximately 70%.
Financial Inclusion Initiatives: Programs such as Aadhaar Enabled Payment Systems (AEPS) and mobile banking services have expanded access to financial services, promoting digital payments across diverse demographics.
Sources:
(2) https://www.ibef.org/blogs/digital-payments-in-india-a-us-10-trillion-opportunity
(3) https://www.ibef.org/download/1649833967_d15e45c9730c1392d810.pdf



Comments